What Is a Multi CDN?
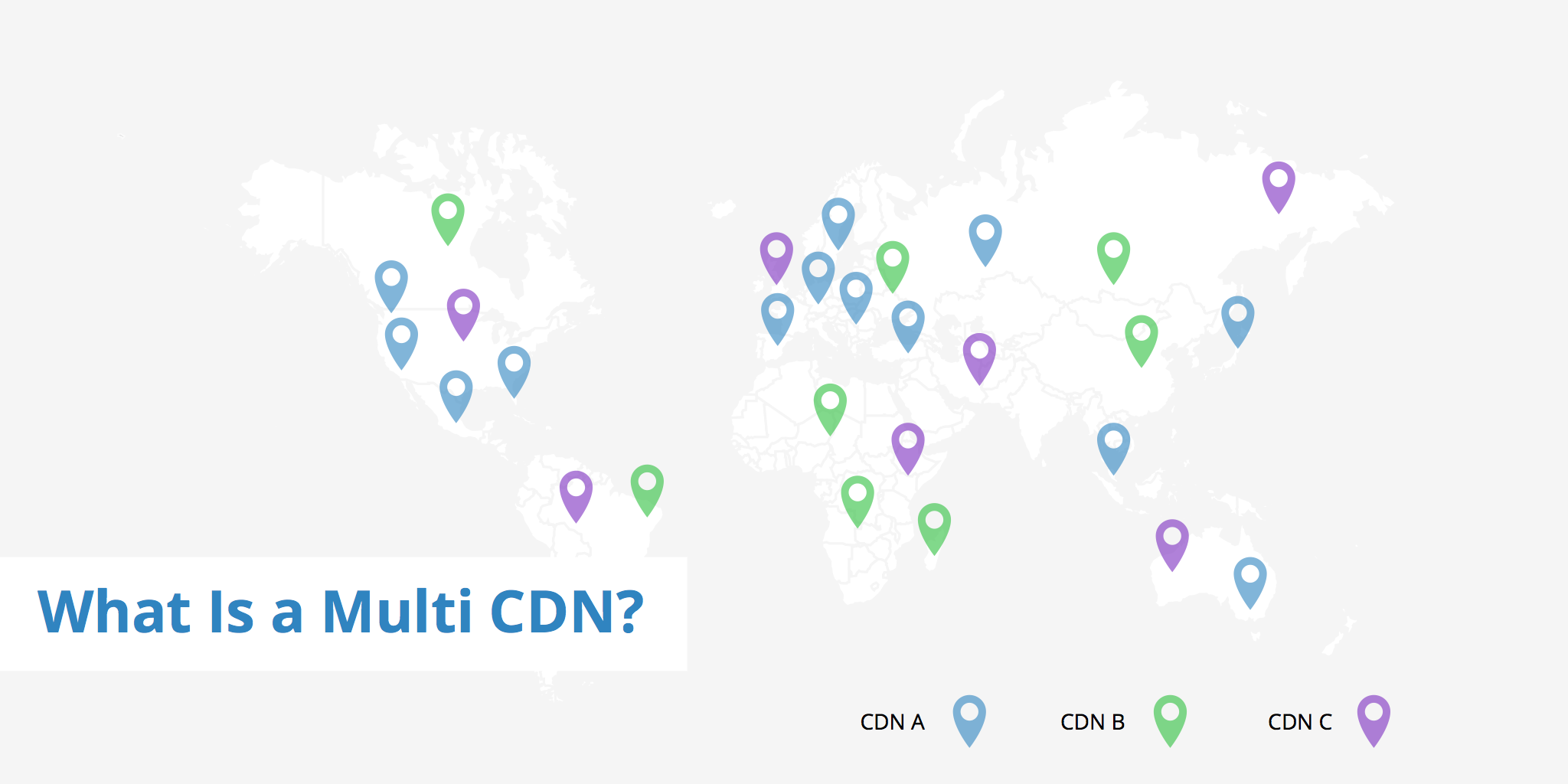
In today's digital world, having a website or an application that is both fast and reliable is essential. Slow loading times and downtime can significantly impact the user experience, which can ultimately result in a loss of revenue and customers. This is where a content delivery network (CDN) comes in, but what about a multi CDN?
Using a multi CDN, or dynamic CDN is the process spreading a website's static content across the servers of multiple CDN providers to further increase global presence. With each CDN provider's servers being available to deliver content, website latency is able to be further reduced for more users in various geographic regions. Having a multi CDN setup in place also helps improve redundancy as if one CDN provider's network goes offline, the content will continue to be delivered from the alternative providers.
This article focuses on how a multi CDN works as well as what the benefits and drawbacks are of using one. For more general information about what a single CDN is and how it works, read our How Does a CDN Work article.
What is a multi CDN?
A multi CDN is essentially a CDN that uses multiple CDN providers to deliver content. Instead of relying on a single CDN, a multi CDN will use several different CDNs simultaneously. This means that when a user requests content, the multi CDN will evaluate which CDN provider is best suited for delivering the content and direct the request to that provider.
There are several reasons why a company may choose to use a multi CDN approach instead of relying on a single CDN provider. One of the main reasons is increased reliability. If one CDN provider experiences downtime or has performance issues, the multi CDN can automatically switch to another provider, ensuring that the content is still delivered to users.
Another reason why a multi CDN may be preferred is increased performance. By using multiple CDN providers, a multi CDN can take advantage of each provider's strengths and weaknesses. For example, one provider may have strong coverage in a specific region, while another provider may have faster response times for a specific type of content.
How does it work?
There are two separate options that can be used to setup a multi CDN configuration. The following section explains how both options work and what is involved in using each.
CDN aggregator
A CDN aggregator combines the functionality of various CDNs and is controllable via one main control panel. There are both benefits and downsides to this. On one hand, you are not required to modify each CDN specifically, which in turn reduces the amount of time required to make a change. On the other hand, this hinders the customizability of each CDN as they are all aggregated into one central control panel.
This method is desirable for companies who aren't seeking to do much customization and don't have a great deal of resources to associate with the administration of a dynamic CDN.
Load balancer: Amazon Route 53
The second option for implementing a multi CDN is to use a load balancer service such as Amazon Route 53. Load balancing is the process of efficiently distributing user requests across multiple servers in order quickly deliver content to a user based on their region as well as to avoid overloading a single server.
Load balancing for a multi CDN is used to distribute requests to the most optimal server within the cluster of servers across various CDNs. Therefore, if a user makes a requests from France their request will be routed to the CDN who's servers are closest to France. Similarly, if a user makes a request from North America, their request will be routed to the most optimal server in the effort to reduce latency times.
Who is using a multi CDN?
The multi CDN strategy has only recently begun to gain traction over the past few years. For large Internet-based companies which deliver content to users around the globe, making use of a multi CDN has proven to be quite beneficial.
Based on Dyn, the top five industry CDN users are also multi CDN users.
| Single CDN industries | Multi CDN industries |
|---|---|
| 1. Internet/Computer software | 1. Internet/computer software |
| 2. Media | 2. Media |
| 3. Retail | 3. Retail |
| 4. Leisure, sports, and recreation | 4. Leisure, sports, and recreation |
| 5. Corporate services | 5. Corporate services |
These industries deliver vast amounts of content to users across the globe and using a multi CDN can help improve the efficiency of that process. It is no surprise that Internet/computer software and media companies are among the top two industries using single and multi CDNs. Companies that stream large media files to their users are able to take great advantage of the widespread global presence of a multi CDN setup. Additionally, software companies like to push their most recent updates to users via a CDN as they will be delivered faster.
Netflix for example uses three CDNs to deliver it's media streaming services to users around the world. YouTube and many other well-known, large technology companies also implement the use of multiple CDNs.
Multi CDN prevails
The usage of multi CDN has evolved significantly over the past few years, driven by a number of factors including increasing demand for fast and reliable content delivery, the rise of cloud-based infrastructure, and the growing complexity of online applications.
Here's a brief overview of how multi CDN usage has evolved:
Early adoption and experimentation (2010-2015)
In the early days of multi CDN, adoption was primarily limited to large enterprises and media companies with significant resources and technical expertise. These companies recognized the potential benefits of using multiple CDN providers to improve content delivery performance, but the complexity and cost of managing multiple providers made adoption challenging.
Widespread adoption and growth (2015-2018)
Over the next few years, the adoption of multi CDN began to accelerate as more companies recognized the benefits of using multiple providers to improve content delivery performance and reduce risk. Advances in cloud-based infrastructure and edge computing also made it easier to manage and optimize multiple CDN providers, further driving adoption.
Standardization and optimization (2018-2023)
In recent years, the usage of multi CDN has continued to evolve as companies have sought to standardize their content delivery strategies and optimize performance across multiple providers. This has led to the development of new standards and protocols for managing and coordinating multiple CDN providers, as well as the adoption of sophisticated load balancing algorithms and real-time analytics tools to ensure optimal performance.
The future of multi CDN (2023 and beyond)
Looking ahead, the usage of multi CDN is expected to continue growing as companies seek to optimize content delivery performance and ensure reliability in the face of increasingly complex online applications. The adoption of new technologies like 5G and edge computing is also expected to drive demand for multi CDN, as companies seek to take advantage of the low latency and high bandwidth capabilities of these new platforms.
Benefits of using a multi CDN
There are obvious benefits to using a multi CDN. The following list describes a few of these benefits:
- Redundancy - Using a multi CDN can ensure that content is always available. If a CDN provider goes down, traffic gets rerouted to another provider's servers
- Increased global presence - By using multiple CDN providers, a multi CDN can leverage the coverage and infrastructure of each provider to reach users in different regions, ensuring that your content is always delivered from the server that is closest to the user.
- Additional features from each CDN - Take advantage of the unique features and capabilities offered by each provider, potentially enhancing the overall content delivery strategy. For example, one CDN provider might specialize in live streaming, while another might be particularly strong in security features like DDoS protection.
- Reduced latency - For users that otherwise would not be as close to a server
- Increased Performance - A multi CDN can improve the performance of content delivery by selecting the fastest CDN provider for each request.
- Better Coverage - A multi CDN can ensure that content is delivered to users all around the world by selecting the CDN provider with the best coverage in a specific region.
- Scalability - A multi CDN can provide greater scalability by allowing companies to easily add or remove CDN providers as their traffic and performance requirements change.
Taking advantage of multiple CDN providers' server locations / performance benefits can be of great value. These advantages are a major reasons why large global companies are adopting the use of dynamic CDNs.
Drawbacks of using a multi CDN
There are also a few drawbacks in using a multi CDN. These drawbacks can include:
- Added complexity - Managing multiple CDN providers can be complex, requiring additional resources and expertise to ensure that everything is properly configured and optimized.
- Added administrative duties - If using the load balancing method
- Additional costs required - While a multi CDN can be cost-effective overall, managing multiple providers can increase costs in terms of setup, integration, and ongoing maintenance.
- Integration challenges - Integrating multiple CDN providers can be challenging, requiring additional development and testing to ensure that everything works correctly.
- Performance Variability - Selecting the fastest CDN provider for each request can result in variability in performance, as different CDN providers may perform differently in different regions or under different conditions.
These drawbacks make it apparent that a multi CDN solution is often not the answer for small, medium, or even certain large sized companies. A website should be receiving a substantial amount of traffic from various locations spread across the globe before beginning to investigate the possibility of implement a multi CDN.
What are federated CDNs?
A federated CDN is different from a multi CDN in that they allow service providers to use preexisting infrastructure to in a way, build their own CDN. Federated CDNs allow service providers to lower costs by pooling resources, minimizing complexity for content providers, and enhancing the consumer's quality of service
Federated CDNs have the objective to:
- Give content providers better control over their content distribution and allow them to offer a better experience to end users
- Reduce network transport costs
- Allow service providers to that don't specialize in CDNs to create a content delivery network
- Simplify business and technical agreements with content providers.
To learn more about CDN Federations, read Cisco's content delivery network (CDN) Federations white paper.
Summary
In summary, multi CDNs are a fantastic solution for distributing content across more servers in even more geographic regions. For the right companies, this method of content distribution is very efficient as users around the world will have more or less equal access to the same speeds.
However, before considering the addition of a multi CDN structure, website owners should first pinpoint website performance issues that may be easily corrected. This may result in enough of a performance increase to avoid opting for a multi CDN although if not, an internal audit based on a company's needs and goals should be undertaken. This will help determine if a multi CDN solution is required or if a single CDN will deliver the required performance without the added complexity.