403 Forbidden Error
We have all encountered the infamous 404 not found error. But what does it mean when you try to access a page, only to be surprised by a message telling you that you don't have permission to access anything on your page? This error occurs when a client accesses a resource for which it does not have permission. Here we will show you the possible causes of the 403 error code and what you can do about it.
What is a 403 Forbidden error?
The 403 Forbidden error is one of many HTTP status codes. What are HTTP status codes? Every time you connect to a web page with your browser, the web server uses what is called an HTTP status code to communicate with your browser. If everything works, the web server responds with a 200 status code. However, you don't notice this; you just get to the web page you have called. However, if something goes wrong, the web server responds with a differently numbered HTTP status code (e.g., 5xx or 4xx).
The web server returns a 403 Forbidden error based on rules configured to tell the server when to deny certain requests. Your server knows what you want, but it won't let you do it for various reasons.
The most common reasons for a 403 Forbidden are:
- IP blocking
- bad file permissions
- trying to access a hidden file
- problem with a plugin or adblocker
Variations of the 403 Forbidden error
There are multiple variations of the 403 error, which you might see dependent upon which server you are using. A few examples include:
- Error 403 Forbidden
- 403 Error
- Forbidden
- 403 Forbidden
- Nginx 403 Forbidden
- 403 Forbidden: Access Denied
- HTTP 403 Forbidden
- 403 Forbidden Error
- 403 Forbidden Nginx
- Forbidden - You do not have permission to access / this server
- 403 - Forbidden: Access has been denied
Differences between 403 Forbidden and 401 Unauthorized errors
Both 401 and 403 errors are similar in that they alert the visitor that they cannot access a resource. However, each error occurs for separate reasons. A 401 error occurs when a request to a particular resource that requires authentication either does not provide authentication or the authentication provided fails.
A 403 error, on the other hand, is returned when the authentication process is passed. Still, the user is not allowed to perform a particular operation, or the operation is forbidden to all users. Examples of operations that may return a 403 Forbidden error are explained in the sections below.
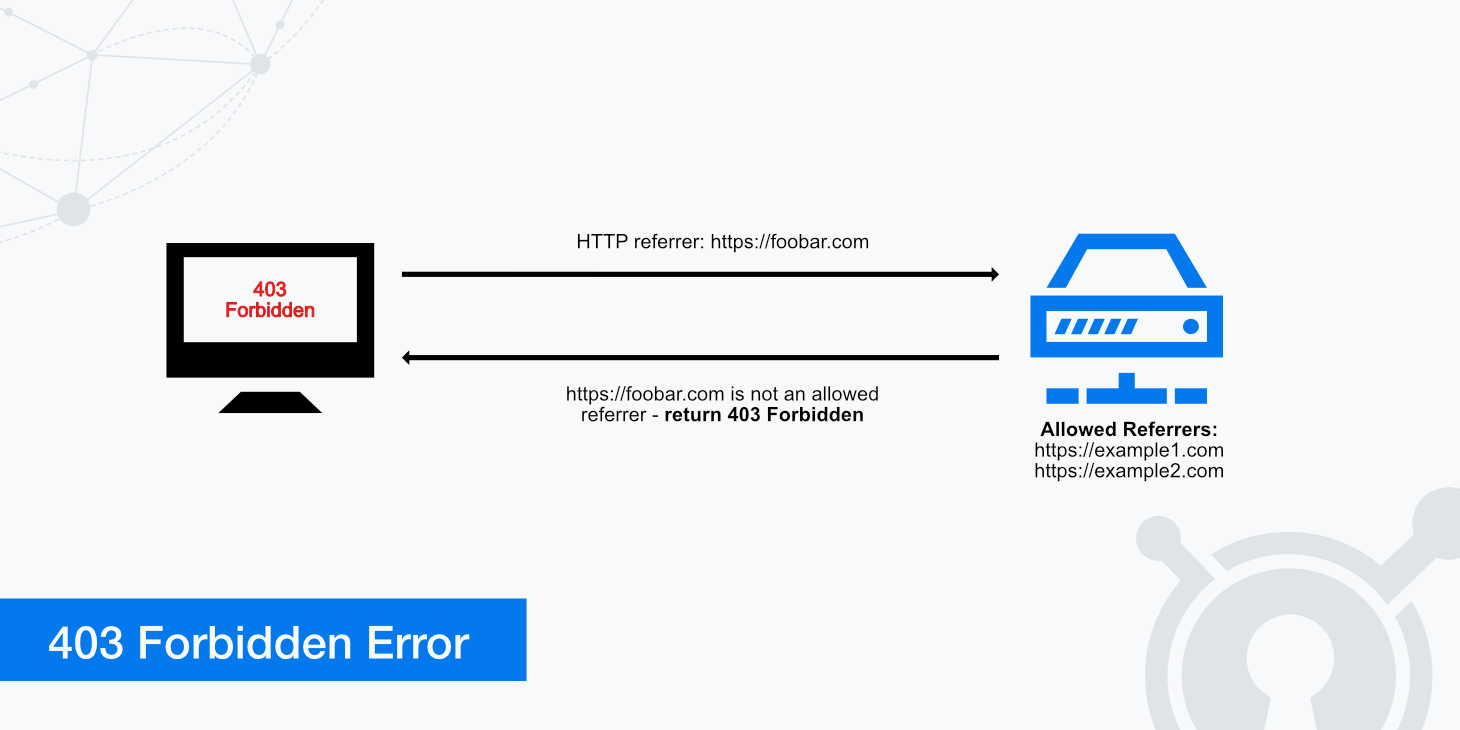
Zone Referrers
Implementing the use of Zone Referrers allows you to restrict HTTP referrers and will return an error 403 to any referrer that you do not specify as a Zone Referrer. This is also known as hotlink protection which can be implemented on your Apache or Nginx server.
KeyCDN offers the feature of implementing Zone Referrers in order to restrict others from referring to the content you have hosted on the CDN and thus won't use your bandwidth. Creating a Zone Referrer is easy and can be done directly from your KeyCDN dashboard.
How to fix 403 Forbidden errors depending on the cause
HTTP 403 Forbidden errors can be caused due to a variety of reasons. The section below identifies a few possible causes and debugging suggestions for this error.
Bad permissions
403 Forbidden errors can occur from file permissions not being set properly. The folders and files on your site's server each have their own file permissions that clearly govern who can do what (read/write/execute). Permissions can be modified using the chmod command in the command line. A quick guideline to the files that should use which permissions are shown below:
- Folders: 755
- Static Content: 644
- Dynamic Content: 700
Secure Token invalid
A Secure Token is a form of authentication that allows a URL to be accessible for a certain period. You can define the expiration time of the token. However, once it expires, the content will no longer be accessible. If the token is invalid, it will return the error 403.
Hotlink protection
As mentioned in the previous section, enabling Zone Referrers within KeyCDN or hotlink protection on your web server will deliver a 403 Forbidden error to referrers who aren't permitted to access your files. Double-check that you have set up your referrers correctly and have added all the domains that should be able to access the website's resources.
Use the HTTP Header Checker tool to test your URL against an HTTP referrer to see if you receive a 403 error as expected.
Caching
A previously requested version of a URL returning a 403 Forbidden error could still be cached in your browser's cache or any intermediary caches. Clearing your cache is a measure you can take to ensure you aren't being served old files.
Hidden files or wrong URL
If a user tries to access hidden files stored on your web server, such as the .htaccess file, this will also return a 403 Forbidden error. Hidden files are not meant to be publicly accessible, so the server restricts them and lets users know they are forbidden to access them. Similarly, suppose a user incorrectly enters a URL. In that case, a 403 Forbidden Nginx error message (or something similar) may also occur depending on what they have entered, for example, a directory instead of a file path.
Check your plugins
It is possible the web server rejected your browser due to various active plugins and/or add-ons (for example, due to the use of an adblocker or proxy plugin). The most efficient way to find the problematic plugin is achieved with an exclusion procedure. You need to deactivate all your plugins and then reactivate them one by one. Once you find the plugin that causes the problem, you can either ask the plugin's developer for help or choose another equivalent plugin.
Firewall settings
If this does not lead to the desired result, there is still a possibility that the web server has a problem with your firewall and therefore gives you the HTTP error 403 in the browser. If you trust the site operator, you can disable the firewall and then try to open the website again. If this solves the problem, you can add an exception for the page in the firewall settings.
Fixing an Nginx 403 Forbidden error
In addition to the 403 error causes mentioned above, there are also a few things you can do to troubleshoot an Nginx 403 Forbidden error.
No index file defined - When there is no index file present in the directory defined with the index directive, this can result in an Nginx
403 Forbiddenerror. For example, consider the following index directive:index index.html index.htm index.php;Nginx will search from left to right for the defined index files. Starting with
index.htmland ending withindex.php, if none of the defined files are found, Nginx will return a403error.IP based restrictions - Your
nginx.conffile should also be verified to ensure you are not unintentionally denying a particular IP. Check the configuration file for directives similar todeny 192.x.x.x;which will block said IP from accessing a particular directory, website, or your complete server (depending on where you define it).Autoindex Off - With Nginx, if you don't have an index file then a request gets passed on to the
ngx_http_autoindex_module. If this module is set to off then you will likely receive an Nginx403 Forbiddenerror. Setting this module to on should resolve the403error. For example:location /directory { autoindex on; }
Summary
HTTP 403 Forbidden errors can happen for various reasons; however, they all mean the same thing - that you are being denied access to the requested resource. Whether you are receiving a 403 Forbidden Nginx error, Apache error, or from any other web server, try debugging the error with the suggestions mentioned above.
If you are not a website operator but a visitor and receive the error message when you visit a website, you should look closely at your browser settings and/or your firewall.
However, website operators protect certain directories of an online offering from "directory browsing". It may also happen that the website administrator has configured the permissions incorrectly. In this case, you have no choice but to contact the website operators and ask for the reason for the 403 error.
If you are using Zone Referrers with KeyCDN and are still getting 403 errors, try consulting our CDN Troubleshooting Guide under Are you getting 403 Forbidden after you enabled Zone Referrers? for more information.